


Contents
1.1 Background
1.2 Reporting Period
1.3 Details of Sampling and Laboratory Testing Activities
1.4 Details of Outstanding Sampling and/or Analysis
1.5 Brief Discussion of the Monitoring Results for ESC CMP V
1.6 Activities Scheduled for the Next Month
1.7 Study Programme
Annexes
Annex A Sampling Schedule
Annex B Water Quality Monitoring Results
Annex C Graphical Presentations
Annex D Study Programme
1.1
Background
1.1.1
The Civil Engineering and
Development Department (CEDD) is managing a number of marine disposal
facilities in Hong Kong waters, including the Contaminated Mud Pits (CMPs) to
the South of The Brothers (SB) and to the East of Sha
Chau (ESC) for the disposal of contaminated sediment, and open-sea disposal
grounds located to the South of Cheung Chau (SCC), East of Tung Lung Chau
(ETLC) and East of Ninepins (ENP) for the disposal of uncontaminated
sediment. Two Environmental Permits (EPs), EP-312/2008/A and EP-427/2011/A,
were issued by the Environmental Protection Department (EPD) to the CEDD, the
Permit Holder, on 28 November 2008 and 23 December 2011 for the Dredging,
Management and Capping of Contaminated Sediment Disposal Facilities at ESC CMP
V and SB CMPs, respectively.
1.1.2
Under the requirements of the two
EPs for ESC CMP V and
SB CMPs, EM&A programmes which encompass water and sediment chemistry,
fisheries assessment, tissue and whole body analysis, sediment toxicity and
benthic recolonisation studies as set out in the
EM&A Manuals are required to be implemented. EM&A programmes have been continuously carried out during the
operation of the CMPs at ESC and SB. A review of the collection
and analysis of such environmental data from the monitoring programme
demonstrated that there had not been any adverse environmental impacts
resulting from disposal activities ([1]) ([2]). The current programme will assess the impacts resulting
from dredging, disposal and capping operations of CMP V as well as capping
operations of SB CMPs.
1.1.3
The present EM&A programme under
Agreement No. CE 63/2016 (EP) covers the dredging, disposal and capping operations of the
ESC CMP V as well as the capping operations of the SB CMPs (see Annex A for the EM&A
programme). The
scheduled EM&A programme for SB CMPs was completed in December 2018.
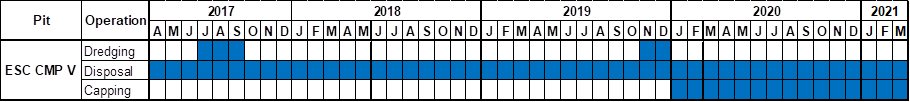
Detailed works schedule for ESC CMP V is shown in Figure
1.1. In September 2020, the
following works were undertaken:
· Disposal of contaminated mud at ESC CMP Vb; and
· Capping operations at ESC CMP Vd.
Figure 1.1 Works Schedule for ESC CMP V
1.2
Reporting Period
1.2.1
This Monthly
EM&A Report for
September 2020 covers the EM&A
activities for the reporting month of September 2020.
1.3
Details of Sampling and
Laboratory Testing Activities
1.3.1
The following monitoring activities
were undertaken for ESC CMP V in September 2020:
· Water Column Profiling of ESC CMP Vb; and
· Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry of ESC CMP Vb.
1.4
Details of Outstanding
Sampling and/or Analysis
1.4.1
No outstanding sampling remained
for September 2020.
1.5
Brief Discussion of the
Monitoring Results for ESC CMP V
1.5.1
Brief discussion of the
monitoring results of the following activities for ESC CMP V is presented in
this Monthly EM&A Report for August 2020:
· Water Column Profiling of ESC CMP Vb; and
· Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry of ESC CMP Vb.
1.5.2
Water Column Profiling of ESC CMP Vb
– September 2020
1.5.3
Water Column Profiling was undertaken at a total of two sampling stations
(Upstream and Downstream stations) on 3 September 2020. The monitoring results have been assessed for
compliance with the Water Quality
Objectives (WQOs) set by Environmental Protection Department (EPD). This
consists of a review of the EPD routine water quality monitoring data for the
wet season period (April to October) of 2009 - 2018 from stations in the Northwestern Water Control Zone (WCZ), where the ESC CMPs
are located ([3]).
For Salinity, the averaged value obtained from the Reference (Upstream) station
was used for the basis as the WQO. Levels of Dissolved Oxygen (DO) and
Turbidity were also assessed for compliance with the Action and Limit Levels
(see Table B1 of Annex B for details).
In-situ
Measurements
1.5.4
Analyses of results for September
2020 indicated that levels of Salinity, pH and DO complied with the WQOs at
both Downstream and Upstream stations (Table
B2 of Annex B). Levels of
DO and Turbidity at all stations complied with the Action and Limit Levels (Tables B1 and B2 of Annex B).
Laboratory Measurements for
Suspended Solids (SS)
1.5.5
Analyses of results September 2020
indicated that the SS levels at both Downstream and Upstream stations complied
with the WQO and the Action and Limit Levels (Tables
B1 and B2 of Annex B).
1.5.6
Overall, the monitoring results
indicated that the mud disposal operation at ESC CMP Vb
did not appear to cause any deterioration in water quality during this
reporting period.
1.5.7
Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry of ESC CMP Vb – September 2020
1.5.8
Monitoring locations for Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry for ESC CMP Vb are shown in Figure
1.2. A total of six (6) monitoring
stations were sampled on 2 September 2020.
1.5.9
The concentrations of most inorganic
contaminants were lower than the Lower Chemical Exceedance Levels (LCELs) at
most stations, except for Arsenic (Figures 1 and 2 of Annex C). The concentrations of Arsenic were higher than the
LCEL at Near-Pit station ESC-NNCA,
Pit-Edge station ESC-NECA and Active-Pit station ESC-NPCB.
1.5.10
Whilst the average concentration of Arsenic in the Earth’s
crust is generally ~2mg/kg, significantly higher Arsenic concentrations (median
= 14 mg/kg) have been recorded in Hong Kong’s onshore sediments ([4]).
It is presumed that the natural concentrations of Arsenic are similar in
onshore and offshore sediments ([5]), and relatively high Arsenic levels may
thus occur throughout Hong Kong. Therefore, the LECL exceedances of
Arsenic are unlikely to be caused by the disposal operations at ESC CMP Vb but rather as a result of naturally occurring deposits.
1.5.11
For organic
contaminants, the concentrations of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) were higher at
Active-Pit station ESC-NPCB
in September 2020 (Figure
3 of Annex C). The concentrations of Low Molecular Weight and High
Molecular Weight Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) were lower than the
LCELs at all stations (Figure
4 of Annex C). The
concentrations of Tributyltin (TBT) were
higher at Active-Pit stations ESC-NPCA and ESC-NPCB (Figure 5 of Annex C). The concentrations of Total Polychlorinated
Biphenyls (PCBs), Total dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT) and 4,4’-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene
(DDE) were below the limit of reporting at all stations in September
2020.
1.5.12
Overall,
there is no evidence indicating any unacceptable environmental impacts to
sediment quality as a result of the contaminated mud disposal operations at ESC
CMP Vb in September 2020. Statistical analysis
will be undertaken and presented in the corresponding quarterly report to
investigate whether there are any unacceptable impacts in the area caused by
the contaminated mud disposal.
1.6
Activities Scheduled for the
Next Month
1.6.1
The following monitoring activities will be conducted in the next
monthly period of October 2020 for ESC CMP V (see Annex A for the sampling schedule ([6])):
· Water Column Profiling of ESC CMP Vb;
· Routine Water Quality Monitoring of ESC CMPs; and
· Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry of ESC CMP Vb.
1.7
Study Programme
1.7.1
A summary of the Study Programme is
presented in Annex D.
([1]) ERM (2013) Final Report. Submitted under Agreement No. CE 4/2009 (EP) Environmental Monitoring and Audit for Contaminated Mud Pit at East Sha Chau. For CEDD.
([2]) ERM (2017) Final Report. Submitted under Agreement No. CE 23/2012 (EP) Environmental Monitoring and Audit for Contaminated Mud Pits to the South of The Brothers and at East Sha Chau (2012 - 2017). For CEDD.
([4]) Sewell RJ (1999) Geochemical Atlas of Hong Kong. Geotechnical Engineering Office, Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region