

Agreement No. CE 23/2012 (EP)
Environmental Monitoring and Audit
for Contaminated Mud Pits at the South of The Brothers
and at
11TH
MONTHLY PROGRESS REPORT FOR JULY 2013
1.1
Background
1.1.1
Since
early 1990s, contaminated sediment ([1])
arising from various
construction works (e.g. dredging and reclamation projects) in Hong Kong has
been disposed of at a series of seabed pits at East of Sha Chau (ESC). In late 2008, a review indicated that
the existing and planned facilities at ESC would not be able to meet the
disposal demand after 2012. In
order to meet this demand, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
Government (HKSARG) decided to implement a new contained aquatic disposal
(CAD) ([2]) facility at the South of The
Brothers (SB CMPs) (hereafter referred to as ¡§the Project¡¨) which had been
under consideration for a number of years.
1.1.2
The
environmental acceptability of the construction and operation of the Project
had been confirmed by findings of the associated Environmental Impact
Assessment (EIA) study completed in 2005 under Agreement No. CE 12/2002(EP) ([3]). The Director of
Environmental Protection (DEP) approved this EIA report under the Environmental Impact Assessment Ordinance (Cap. 499) (EIAO) in September 2005 (EIA
Register No.: AEIAR-089/2005).
1.1.3
In
accordance with the EIA recommendation, prior to commencement of construction
works for the SB CMPs, the Civil Engineering and Development Department (CEDD)
undertook a detailed review and update of the EIA findings for the SB site ([4]). Findings of the EIA review undertaken in
2009/ 2010 confirmed that the construction and operation of the SB site had
been predicted to be environmentally acceptable.
1.1.4
Environmental
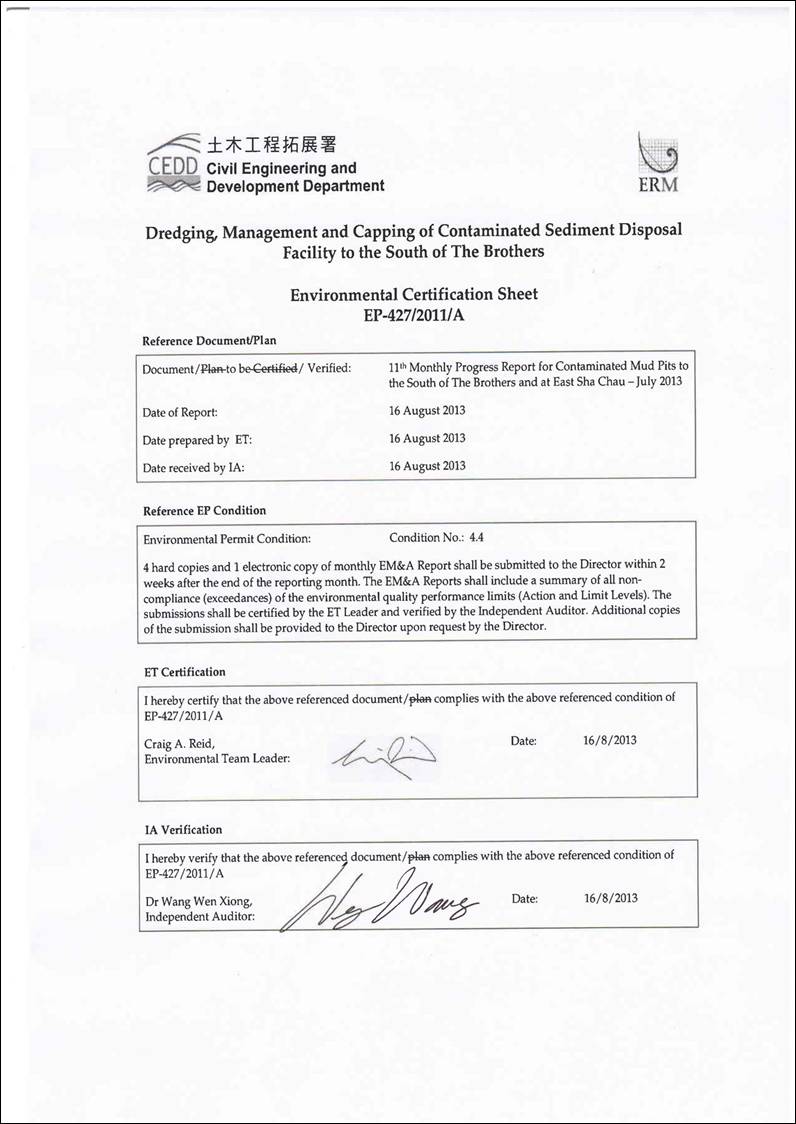
Permits (EPs) (EP-312/2008/A and EP-427/2011A) were issued by the Environmental
Protection Department (EPD) to the CEDD, the Permit Holder, on 28 November 2008
for ESC CMP V and on 23 December 2011 for SB CMPs respectively. Under the requirements of the EPs, an Environmental Monitoring and Audit (EM&A) programme as set out
in the EM&A Manuals ([5])([6])
is required to be
implemented for the CMPs.
1.1.5
The present EM&A programme undertaken under Agreement No. CE 23/2012 (EP)
covers the dredging, disposal and capping operations of the SB CMPs as well
as CMPs at East of Sha Chau (ESC). In July
2013, the following works were being undertaken at the CMPs:
¡P
Capping was being undertaken at
CMP IVc;
¡P
Disposal of contaminated mud was
taking place at CMP Va; and
¡P
Dredging operations were taking place at
SB CMP 1.
1.2
Reporting Period
1.2.1
This
Monthly Progress Report covers the EM&A activities
for the reporting month of July 2013.
1.3
Details of Sampling and
Laboratory Testing Activities
1.3.1
The following monitoring activities have been
undertaken for CMP V in July 2013:
¡P
Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry was
conducted for CMP Va on 3 July 2013;
¡P
Water Column Profiling was scheduled
to be undertaken on 9 July 2013.
However, there was no dumping activity at CMP Va while the monitoring
team was on-site. As such, in-situ measurements and water sampling
were not undertaken for Water Column
Profiling in July 2013;
¡P
Routine Water Quality Monitoring
was conducted for CMP Va on 16 July
2013; and
¡P
Demersal Trawling was conducted for CMP V
on 30 and 31 July 2013.
1.3.2
Impact Water Quality Monitoring during Dredging
Operations of CMP 1 was conducted three times per week (ie 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 17, 19, 22, 24, 26, 29 and 31 July 2013) in this reporting month in
accordance with the EM&A Manual.
It should be noted that the Impact Water Quality Monitoring during
Dredging Operations of CMP 1 was not conducted on 1 July 2013 due to the
adverse weather during which Typhoon signal No. 3 was hoisted.
1.4
Details of Outstanding Sampling and/or Analysis
1.4.1
No outstanding sampling remained for July 2013. Laboratory
analyses of Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry of CMP Va conducted in June and July 2013 were yet to
be completed and laboratory analyses of Suspended Solids (SS) for Water Quality
Monitoring during Dredging Operations of CMP 1 collected
on 31 July 2013 was still in progress during the preparation of this monthly
report. A summary of field
activities conducted are presented in Annex
A.
1.5
Brief Discussion of the Monitoring Results for CMP V
1.5.1
Table 1.1 summarises the monitoring
results that are presented in the current monthly report. Brief discussion of the
monitoring results is presented in this section. Detailed discussion will be presented in
the corresponding Quarterly Report.
|
Monitoring
activities |
Date
of Monitoring |
Monitoring results presented in this report? |
|
Pit
Specific Sediment Chemistry Monitoring for CMP Va |
14 May 2013 3 July 2013 |
Yes. No. Laboratory analysis yet to be
completed during preparation of this monthly report. No. Laboratory analysis yet to be
completed during preparation of this monthly report. |
|
Routine Water
Quality Monitoring for CMP Va |
16 July 2013 |
Yes. |
|
|
|
|
|
Water
Column Profiling for CMP Va |
9 July 2013 |
No. In-situ measurements and water
sampling were not undertaken as there was no dumping activity on the
monitoring day. |
Table
1.1 Monitoring
activities in May to
July
2013 for CMP V
1.5.2
Pit Specific
Sediment Chemistry of CMP Va ¡V May 2013
1.5.3
Monitoring locations for Pit Specific Sediment
Chemistry for CMP Va are shown in Figure
1.1. A total of six
monitoring stations were sampled in May 2013. It is observed that the variations of
metal concentrations at Active Pit Stations NPDA and NPDB were
much larger (ie greater standard deviation) when compared to other stations (Figures 1-2 of Annex B).
1.5.4
Cadmium, Chromium and Nickel
complied with the Lower Chemical Exceedance Level (LCEL) at all stations (Figures 1-2 of Annex B). Concentrations of Arsenic exceeded the
LCEL at Pit Edge stations NEDA and NEDB and Near Pit stations NNDA
and NNDB (Figures
1-2 of Annex B). Concentrations of Lead, Mercury and
Zinc exceeded LCEL at Active Pit station NPDA while
concentrations of Silver exceeded Upper Chemical Exceedance Level (UCEL) at
Active Pit stations NPDA and NPDB. Concentration of Copper exceeded
UCEL at Active Pit Station NPDA.
1.5.5
Whilst the average concentration of Arsenic in the
Earth¡¦s crust is generally ~2mg/kg, significantly higher Arsenic concentrations
(median = 14 mg/kg) have been recorded in Hong Kong¡¦s onshore sediments ([7]). It is presumed that
the natural concentrations of Arsenic are similar in onshore and offshore
sediments ([8]), and
relatively high Arsenic levels may thus occur throughout Hong Kong. Therefore, the exceedances of the
LCEL for Arsenic are unlikely to be caused by the disposal operations at CMP Va
but rather as a result of naturally occurring deposits.
1.5.6
In addition, the Active Pit stations NPDA and
NPDB are located within CMP Va which was receiving contaminated mud
during the reporting period. As
such, the exceedances of LCEL/UCEL for Copper, Lead, Mercury, Silver and
Zinc which were recorded at the two stations only are not
considered as indicating any dispersal of contaminated mud from CMP Va.
1.5.7
For organic contaminants, Total
Organic Carbon (TOC) concentration was similar amongst all stations (Figure 3
of Annex B). Tributyltin (TBT) concentration was
found to be higher at Active Pit stations NPDA and NPDB (Figure 4
of Annex B). Low Molecular Weigh Polycyclic Aromatics
Hydrocarbons (Low MW PAHs) and High Molecular Weight Polycyclic Aromatics
Hydrocarbons (High MW PAHs) concentrations were recorded above the limit of
reporting at Active Pit stations NPDA
and NPDB (Figure 5 of Annex B). Total Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs),
Total Dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT) and
4,4¡¦-Dichloro-diphenyl-dichloroethylene (4,4¡¦-DDE) were below the limit of
reporting at all stations. As explained in Section
1.5.6, Active Pit
stations NPDA and
NPDB are located within CMP Va which was receiving contaminated mud during the
reporting period. Therefore, the
higher concentrations of contaminants (including metals and organic
contaminants) recorded at the two stations only are not considered as
indicating any dispersal of contaminated mud from CMP Va. Nevertheless, detailed analysis will be
presented in the Quarterly Report to reveal any trend of increasing
sediment contaminant concentrations towards CMP Va.
1.5.8
Overall, there is no evidence
indicating any unacceptable environmental impacts to sediment quality as a
result of the contaminated mud disposal operations at CMP Va during this
monthly period.
1.5.9
Routine Water Quality
Monitoring for CMP Va ¡V July 2013
1.5.10
The results for the Routine Water Quality Monitoring
conducted during July 2013 in the wet season have been assessed for
compliance with the Water Quality Objectives (WQOs) set by Environmental
Protection Department (EPD). This
consists of a review of the EPD routine water quality monitoring data for the
wet season period (April to October) of 1999-2010 from stations in the
Northwestern Water Control Zone, where the CMPs are located. For Salinity, the average value obtained
from the Upstream Station was used for the basis as the WQO. In-situ monitoring and laboratory
results are shown in Tables 1.2 and 1.3, respectively, with graphical presentation provided in Annex B. Monitoring was undertaken at a total of
10 stations in the reporting month (see Figure
1.2).
In-situ
Measurements
1.5.11
Analysis of results for July 2013
indicated that for all stations (Impact, Intermediate, Reference and Ma Wan),
levels of pH and DO complied with the WQOs (Figures 6 and 7 of Annex B). Levels
of Salinity complied with the WQO at all stations, except at Ma Wan Station (Figure 9 of Annex B).
The higher salinity recorded at Ma Wan station is likely to be caused by
its greater separation distance from the Pearl River mouth, which is a key source
of freshwater inputs in the area, when compared to the Reference stations. Levels of DO and Turbidity within the
reporting month complied with the Action and Limit Levels set in the EM&A Manual ([9])
(Figures
7 and 10 of Annex B). All in-situ water
quality measurements showed relatively minor variations amongst Impact,
Intermediate and Reference stations (Figures 6-10 of Annex B).
Laboratory
Measurements
1.5.12
Analyses of July 2013 results indicate
that concentrations of Cadmium, Mercury and Silver were below their limit of
reporting at all stations while Arsenic, Chromium, Copper, Lead, Nickel
and Zinc were detected in samples from all stations. Concentrations of Chromium,
Copper, Lead, Nickel and Zinc were slightly higher at
Ma Wan station while the concentrations of Arsenic were similar
amongst stations (Figures 11 and 12 of Annex
B). Levels of 5-day Biochemical Oxygen
Demand (BOD5), Total Inorganic Nitrogen (TIN) and
Ammoniacal-Nitrogen (NH3-N) were similar amongst all stations (Figures 13 and 14 of Annex B).
Concentrations of Suspended Solids (SS)
complied with the WQO (12.74 mg/L for wet season) and Action and Limit Levels
at all stations during the reporting month (Figure 15 of Annex B).
1.5.13
Overall, the results indicated that the disposal
operation at CMP Va did not appear to cause any unacceptable deterioration in
water quality during this reporting period.
Table 1.2 In-situ
Monitoring Results for Routine Water Quality Monitoring of CMP Va in July 2013
|
Stations |
Temp |
Salinity |
Turbidity |
pH |
Dissolved Oxygen |
|
|
|
(¢XC) |
|
(NTU) |
|
(%) |
(mg L-1) |
|
RFF
(Reference) |
28.05 |
22.05 |
2.05 |
7.69 |
59.95 |
4.18 |
|
IPF
(Impact) |
27.67 |
23.28 |
3.90 |
7.65 |
65.10 |
4.50 |
|
INF
(Intermediate) |
27.76 |
23.23 |
2.86 |
7.65 |
65.39 |
4.51 |
|
Ma
Wan Station |
26.13 |
27.90 |
1.58 |
7.54 |
59.51 |
4.12 |
|
WQO |
N/A |
19.85-24.26# |
N/A |
6.5-8.5 |
N/A |
>4 |
|
Note:
#Not
exceeding 10% of natural ambient level which is the result obtained from the
Reference Station. |
||||||
Table 1.3 Laboratory
Results for Routine Water Quality Monitoring of CMP Va
in July 2013
|
Stations |
As (µg/L) |
Ag (µg/L) |
Cd (µg/L) |
Cr (µg/L) |
Cu (µg/L) |
Hg (µg/L) |
Pb (µg/L) |
Ni (µg/L) |
Zn (µg/L) |
NH3-N (mg/L) |
TIN (mg/L) |
BOD5 (mg/L) |
SS (mg/L) |
|
|
|
RFF
|
1.58 |
<LOR |
<LOR |
0.63 |
8.08 |
<LOR |
0.98 |
3.29 |
10.29 |
0.08 |
0.95 |
0.36 |
4.00 |
|
|
|
IPF
|
1.96 |
<LOR |
<LOR |
0.90 |
10.75 |
<LOR |
1.13 |
2.75 |
11.25 |
0.08 |
0.75 |
0.29 |
5.38 |
|
|
|
INF
|
1.75 |
<LOR |
<LOR |
0.56 |
8.25 |
<LOR |
0.65 |
2.13 |
8.33 |
0.10 |
0.89 |
0.27 |
4.46 |
|
|
|
Ma
Wan Station |
1.50 |
<LOR |
<LOR |
1.88 |
21.25 |
<LOR |
1.88 |
4.00 |
20.00 |
0.06 |
0.53 |
0.25 |
3.75 |
|
|
|
|
WQO of SS: 12.74 mg/L |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Note: LOR = Limit Of Reporting |
|
||||||||||||||
1.6
Brief Discussion of the Monitoring Results for SB CMPs
1.6.1
Monitoring data collected for SB
CMPs in July 2013
are presented in this monthly report.
Detailed discussion will be presented in the corresponding Quarterly Report.
1.6.2
Impact Water
Quality Monitoring during Dredging Operations of CMP 1 ¡V 4 to 29 July 2013
1.6.3
Impact Water Quality Monitoring during Dredging Operations
of CMP 1 was conducted three times per week for a total of
twelve (12) sampling
days from 4 to 29 July 2013. On each survey day, sampling was
conducted during both mid-ebb and mid-flood tides at two Reference (Upstream)
stations upstream and five Impact (Downstream) stations downstream of the
dredging operations at CMP 1.
Monitoring was also conducted at five Sensitive Receiver Stations (Ma
Wan, Shum Shui Kok, Tai Mo To and Tai Ho Bay). A total of twelve stations were
monitored and locations of the sampling stations are shown in Figure 1.3.
1.6.4
Monitoring results from 4 to 29 July 2013 are presented in Table C1 of Annex C. It should be noted that sampling at
station THB2 during mid-ebb tide on 24
July 2013 and
during both mid-ebb and mid-flood
tides on 26 July
2013 were not carried out due to adverse weather. Levels of DO, Turbidity and SS generally
complied with the Action and Limit Levels (see Table C2 for details) set in the Baseline Monitoring Report ([10]),
except for the following occasions of exceedances shown in Table 1.4 below.
Table 1.4 Details
of exceedances recorded at CMP 1 in July 2013
|
Date |
Tide |
Parameter |
Station |
Type |
|
22 July
2013 |
Mid-Ebb |
Turbidity |
WSR46 |
Action |
|
22 July 2013 |
Mid-Ebb |
SS |
WSR46 |
Action |
|
26 July 2013 |
Mid-Ebb |
Turbidity |
WSR46 |
Action |
|
26 July 2013 |
Mid-Ebb |
SS |
WSR46 |
Limit |
|
26 July 2013 |
Mid-Flood |
SS |
WSR46 |
Action |
1.6.5
Action/Limit Level exceedances of
Turbidity and SS were recorded at Sensitive
Receiver station WSR46
during mid-ebb tide on 22 July
and during both mid-ebb and mid-flood tides on 26 July 2013. Station WSR46 is located further away from the
works area of CMP 1 when compared to station DS1 at which the levels of SS and
Turbidity did not exceed the Action and Limit Levels during the same tidal
period. As such,
the exceedances at WSR46 are not likely to be caused by the dredging works at
CMP 1. It should be noted that high
levels of Turbidity and SS were occasionally recorded during baseline
monitoring which are considered to be sporadic events and characteristic of
water quality in this area of Hong Kong.
Therefore, the Action and Limit Level exceedances may be caused by
natural background variation in water quality of the area.
1.6.6
Overall, the results indicated that
the dredging operations at CMP 1 of SB did not appear to cause any unacceptable
deterioration in water quality during this reporting period. Therefore, no further mitigation
measures, except for those recommended in the Environmental Permit (EP-427/2011/A),
are considered necessary for the dredging operations.
1.7
Activities Scheduled for the
Next Month
1.7.1
The following monitoring activities will be conducted
in the next monthly period of August 2013 for CMP V:
¡P
Pit Specific Sediment Chem-istry for CMP Va;
¡P
Cumulative Impact Sediment Chemistry for CMP Va;
¡P
Sediment Toxicity Test for CMP Va;
¡P
Routine Water Quality Monitoring for
CMP Va;
¡P
Water Column Profiling for CMP
Va; and
¡P
Demersal Trawling for CMP V.